How does CBD work in the body? Receptors as Cellular Gatekeepers (th translation)


- The ECS is comprised of two types of receptors, CB1 and CB2, which respond positively to the co mpounds naturally produced by our bodies and plants called cannabinoids
- Receptors are critical parts of the ECS and are found on all cell surfaces. They act as our “cellular gatekeepers”
- Present in cell membranes throughout the body
- Human breast milk is an abundant source of endocannabinoids, a specific type of neuromodulatory lipid that basically teaches a newborn child how to eat by stimulating hunger and the suckling process



- Present in cell membranes throughout the body
- Human breast milk is an abundant source of endocannabinoids, a specific type of neuromodulatory lipid that basically teaches a newborn child how to eat by stimulating hunger and the suckling process


Lock and Key Relationship
- CBD, CBN, and THC fit like keys into existing human receptors
- CBD does not directly “fit” CB1 or CB2, but has powerful indirect effects still being studied
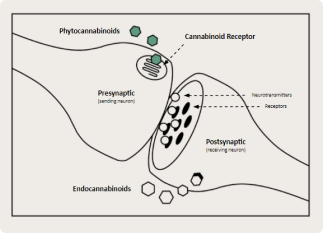

Mechanism of Actions
- Phytocannabinoids bind to receptors in the body to stimulate, supplement, and support our ECS and homeostasis.
- They take stimuli from outside of the the cells in the body and convert them to signals inside our cells.